Key facts and concepts
What is PSD2?
This term is short for 'Payment Services Directive 2.' It refers to the Directive (EU) 2015/2366 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 November 2015 on payment services in the internal market, adopted in November 2015. This is the second such document, which is an extension and replacement of the existing (in force since 2007) Directive 2007/64/EC - the so-called PSD1. The new directive is a response to rapid changes in the payment services market resulting from the use of modern technologies and services, for which the previously applicable regulations were no longer sufficient. All EU member states, including Poland, have been given two years to comply with the provisions of the new directive. The regulations resulting from the PSD2 were introduced to the Polish legal system by an amendment to the Payment Services Act of 5 June 2018.
What is the purpose of introducing PSD2?The main goals are:
- To ensure even greater security of transactions by, among other things, introducing the obligation to use the so-called SCA (Strong Customer Authentication) mechanisms;
- To increase consumer protection by increasing the liability of service providers for unauthorised transactions and regulating and supervising new payment services;
- To establish international standards for payment transactions and unify the EU payments market;
- To introduce new categories of service providers that can provide additional services, requiring consent to access information about the Customer's account - the so-called TPP (Third Party Providers).
What does the PSD2 introduce?
The Directive introduces a number of new rules and obligations for all financial institutions that process payments, as well as for entities accepting payments within the European Economic Area. Among the main changes and new solutions introduced by the directive, you should pay particular attention to the following:
- No additional fees/commissions charged for payment by consumer payment card (surcharge for the use of business cards will still be allowed).
- Introduction of SCA - Strong Customer Authentication used to authorise card payments on terminals and payments on the Internet and mobile applications.
What is SCA?
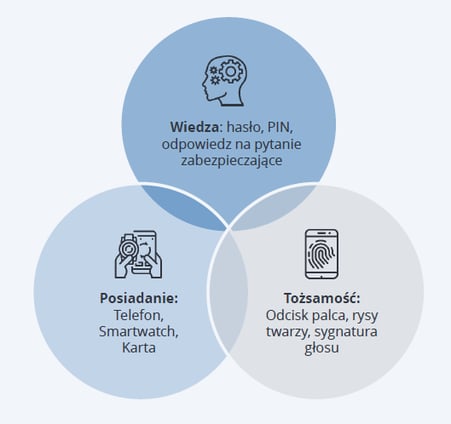
SCA - Strong Customer Authentication is a relatively recent term that is part of the PSD2 Directive. In simple terms, it can be said to be a two-factor payment transaction authentication that consists of at least two elements belonging to a category:
- Knowledge - the authorisation must be based on information known only to the user - e.g. the PIN code;
- Possession - for authorisation you need something that can only be possessed by the user - e.g. a card or a phone;
- Identity - authorization may require confirmation of features characteristic only for the card holder - fingerprint, facial features, voice (biometric solutions).
This will make it necessary to use a card or smartphone to confirm some transactions and enter the PIN code or use a card or smartphone and enter the confirmation code sent by SMS.
Similar rules will apply to payment transactions for purchases made over the internet or mobile applications, i.e. without the physical presence of a card or any other medium. In their case, it will be necessary to authorise transactions using 3-D Secure solutions.
What is 3-D Secure and where to get it from?
3-D Secure is a security enhancing method for authorising transactions carried out without physical use of the card (i.e. using only the card's data - number, user's first name and surname, expiry date and CVV code on the back of the card). 3-D Secure solutions are available, among others, from the largest payment organizations - Visa, MasterCard, American Express and JCB.
The 3-D Secure transaction is secured by identification and confirmation of the card holder's rights. This is usually done using a one-time password generated by means of a token or sent by SMS to a phone number assigned to the cardholder's account. Elimination of the risk of unauthorized use of the card in this way makes the cardholder fully responsible for transactions made with 3-D Secure.
Requirements for transaction authorization with 3D Secure:
- Transactions must be authenticated using at least two of the three factors above.
- The factors must be independent of each other and belong to different categories, e.g. loss of phone does not automatically mean compromise of password.
- In the case of remote payments, the authentication must be assigned to a specific amount and recipient - the so-called Dynamic Linking.
Customers using the eCommerce payment gateway in eService are provided with 3-D Secure service as part of the service.
What are the risks of not complying with PSD2/SCA requirements?
Non-compliance with the requirements of the new regulations has a number of consequences. Among them, the following are of particular importance:
- Inability to accept non-cash payments from customers;
- Inability to sell goods and services by electronic means (Internet, applications) - decrease in revenue, inability to implement sales plans;
- Dissatisfaction and loss of customers who cannot shop and order services;
- Loss of the image of a well-organized, efficient company;
- Financial penalties imposed by payment organisations in the event of a breach of the obligations imposed by the PSD2.

